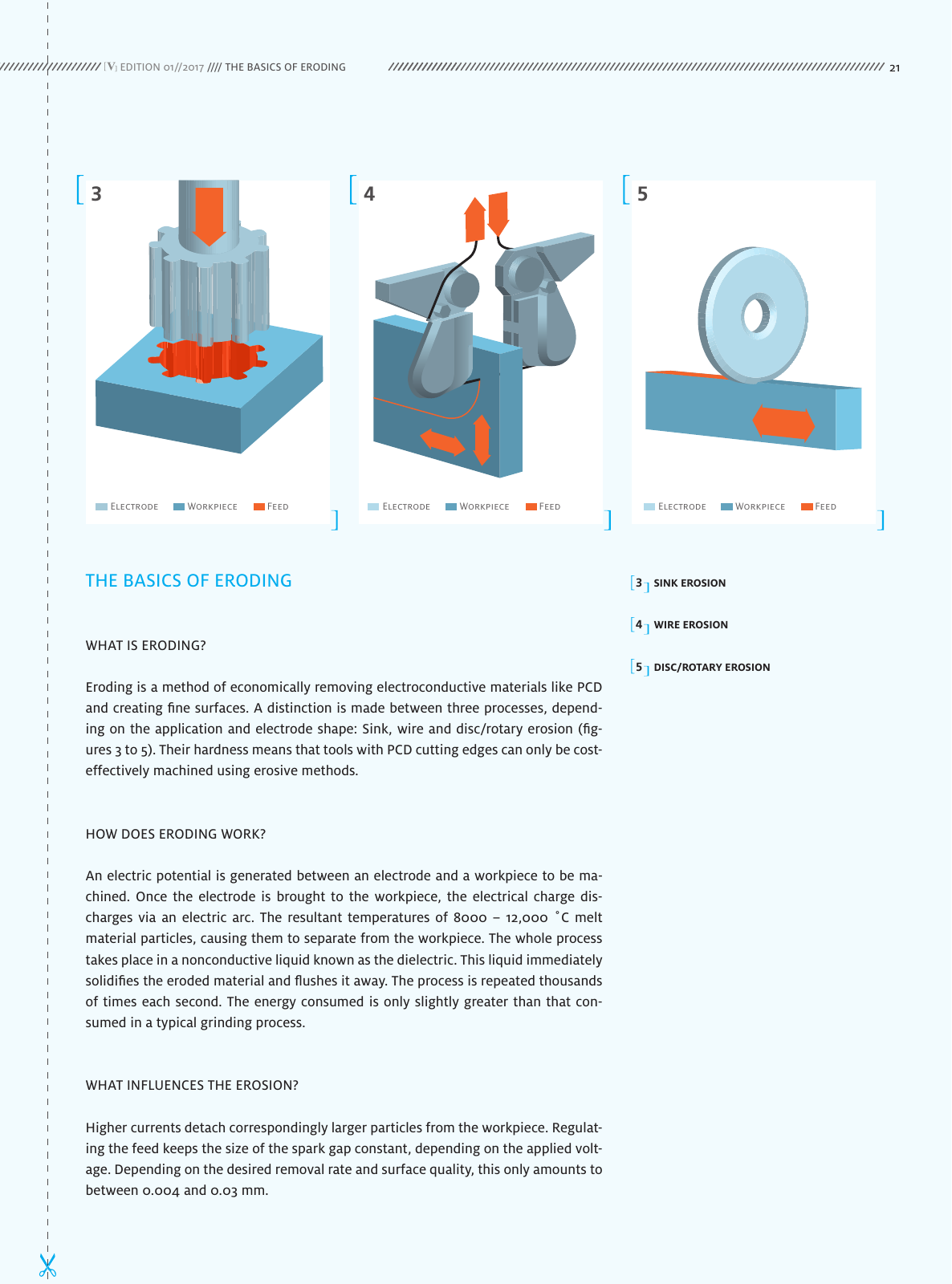
THE BASICS OF ERODING WHAT IS ERODING Eroding is a method of economically removing electroconductive materials like PCD and creating fine surfaces A distinction is made between three processes depend ing on the application and electrode shape Sink wire and disc rotary erosion fig ures 3 to 5 Their hardness means that tools with PCD cutting edges can only be cost effectively machined using erosive methods HOW DOES ERODING WORK An electric potential is generated between an electrode and a workpiece to be ma chined Once the electrode is brought to the workpiece the electrical charge dis charges via an electric arc The resultant temperatures of 8000 12 000 C melt material particles causing them to separate from the workpiece The whole process takes place in a nonconductive liquid known as the dielectric This liquid immediately solidifies the eroded material and flushes it away The process is repeated thousands of times each second The energy consumed is only slightly greater than that con sumed in a typical grinding process WHAT INFLUENCES THE EROSION Higher currents detach correspondingly larger particles from the workpiece Regulat ing the feed keeps the size of the spark gap constant depending on the applied volt age Depending on the desired removal rate and surface quality this only amounts to between 0 004 and 0 03 mm 3 4 5 Electrode Workpiece FeedElectrode Workpiece FeedElectrode Workpiece Feed EDITION 01 2017 THE BASICS OF ERODING 3 SINK EROSION 4 WIRE EROSION 5 DISC ROTARY EROSION 21
Hinweis: Dies ist eine maschinenlesbare No-Flash Ansicht.
Klicken Sie hier um zur Online-Version zu gelangen.
Klicken Sie hier um zur Online-Version zu gelangen.